CANCER OF THE CERVIX
Cancer is an excessive growth of any body tissue with a capability of spreading to other parts of the body. The cervix is the lower, narrow part of the uterus (womb). The cervix forms a canal that opens into the vagina, which leads to the outside of the body.
Why is it important to diagnose and prevent?
It is the most common cause of cancer in women in India with more than 72,000 deaths/year Over 200 women die from Cervical Cancer every day. On an average 8 woman die every hour and 1 woman dies every 7 minute.Who is at risk in developing cancer of the cervix?
• Initiation of sexual intercourse before age 18 • Multiple sexual partners • Early age of marriage • First pregnancy at an early age • Four or more number of pregnancies • Women with poor personal hygieneWhat are the symptoms of cervical cancer?
• Bleeding after sexual intercourse or in between periods • Bleeding after menopause (menopause is the period after cessation of periods) • Excessive white discharge (leucorrhoea) could be an early symptom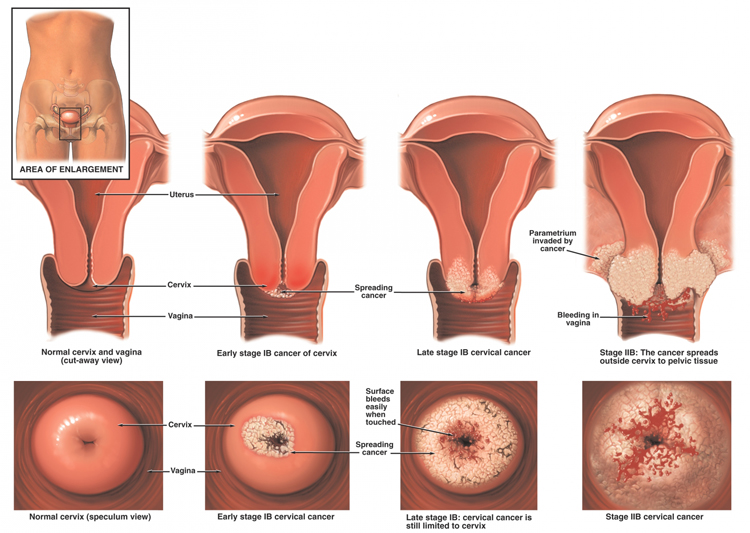
How can cancer of the cervix be diagnosed?
When you visit a doctor with any of the above problems, the doctor will ask you questions about your symptoms and will examine you. The tests for detection of cervical cancer include Pap smear, colposcopy and cervical biopsyPap Smear
The Pap smear is a test to detect early changes in cells of the cervix (Pre-cancer stage). It is taken during an internal examination of the vagina. A speculum is inserted into the vagina and some cells are then taken from the cervix using a small brush and sent to a medical laboratory to be checked for abnormal cells (Cytology) It is not a painful procedure.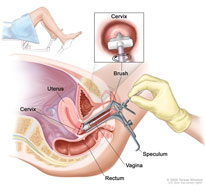 Colposcopy: Microscopic examination of the cervix to look for abnormal areas.
Biopsy of the cervix is removal of a piece of tissue for laboratory examination (Histology)
Colposcopy: Microscopic examination of the cervix to look for abnormal areas.
Biopsy of the cervix is removal of a piece of tissue for laboratory examination (Histology)
